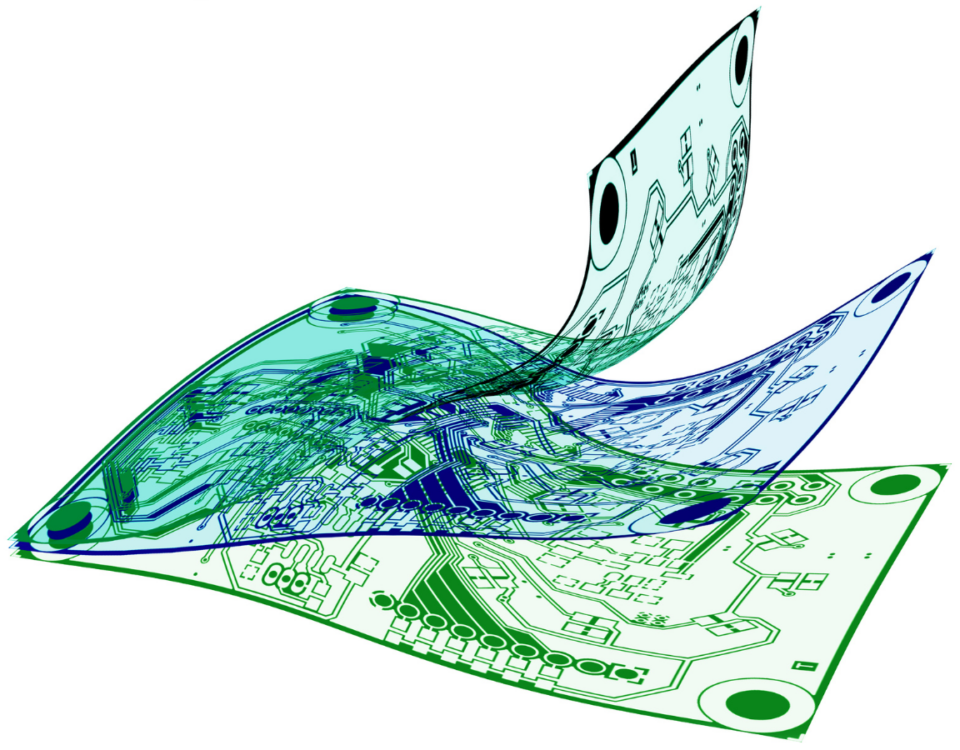
What Are Conductive Inks?
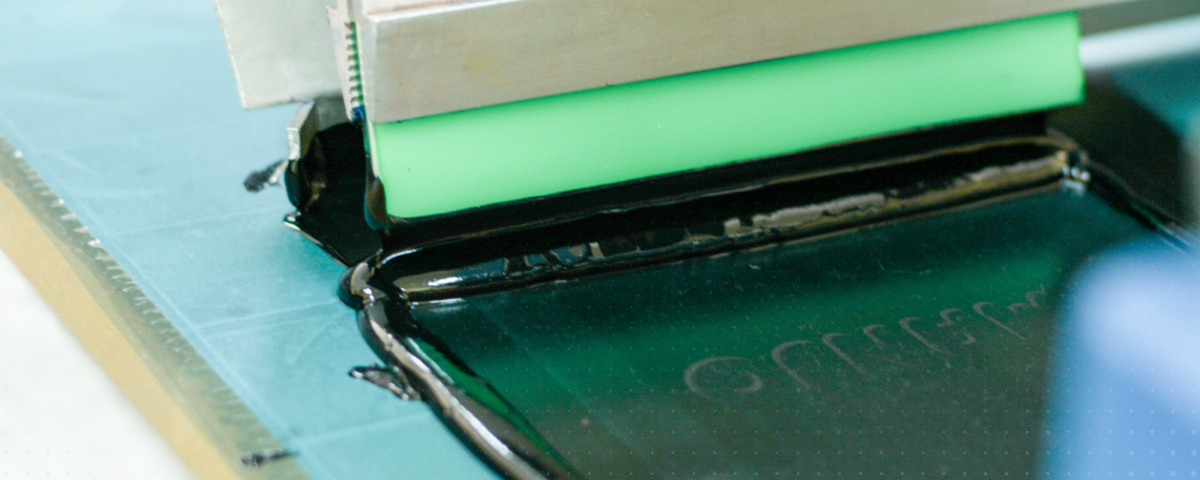

Conductive inks are revolutionizing the printing world by allowing thin, flexible circuits to be printed on various materials. Conductive inks are the ideal material for wearables and printed electronics.
The science behind conductive inks has come a long way since they were first introduced in the early 1990s. Modern inks offer several advantages over traditional percolation conductors.
What are Conductive Inks?
Conductive inks are made from silver or carbon particles that conduct electricity. These inks can replace traditional wired or copper circuits in electronics.
These inks can be used to additively manufacture circuits using screen printing processes or direct-write technology to print fine-line traces on substrates like PET, PC, TPU, etc. The inks are compatible with various printing methods and can be tailored to your specific application.
Different Types of Conductive Inks
There are three main types of conductive inks used to make printed electronics. These include the traditional percolation conductor, sinterable conductors, and a new semi-sintering conductor that offers several advantages over traditional inks.
Percolation Conductors
Traditional conductive ink is a percolation conductor or polymer thick film (PTF) conductor. These inks are used commercially to make printed electronics. They are comprised of conductive fillers dispersed at high loadings into thermoplastic polymers that have been dissolved in a solvent.
These inks have good adhesion to the substrate material due to the amount of polymer wetting the substrate interface. However, they have weak electrical performance. The polymers and organic stabilizers on the particles create contact resistance diminishing electrical performance. At best, these traditional inks can only typically achieve the volume resistivity of lead.
Sinterable Conductors
Sinterable conductors have been developed in the last 20 years. These inks sinter together to avoid the contact resistance seen in percolation conductors. Therefore, they provide higher electrical conductivity than traditional inks.
The challenge with sinterable conductors is formulating them with enough resin to wet the substrate well. It is also challenging to drive sintering at equivalent temperatures to which PTF conductors can be dried. Although these conductors have been commercially available for decades and perform well in a lab, few have been used in commercial electronic devices.
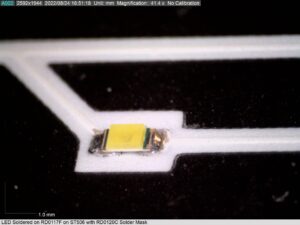
Alchemy Conductors
ACI Materials developed a new series of inks that combines the best of both percolation conductors and sinterable conductors. Alchemy conductive inks are hybrid or semi-sintering conductors. These inks have the ease of use and the curing and process time of a polymer thick film but with the electrical conductivity of sinterable inks.
Alchemy inks allow lower usage of silver and thus cost reduction. They also offer several other benefits over traditional conductive inks including:
- Lower sheet resistance compared to PTF, nanoparticle, and metal complex-based inks
- Faster cure times than traditional nanoparticle-based sinterable inks
- Nano-like volume resistivity (conductivity), but in less time
- Superior hard crease survivability compared to even PTF inks
- Allow high-resolution printing without compromising resistivity and sheet resistance
- Enables reflow soldering using low-temperature solder pastes
- Thinner EMI shielding coatings
ACI Materials’ scientists continue to perfect the alchemy inks making them the leading ink for high-performance flexible hybrid electronics and more. Alchemy conductive inks could also reduce the cost per device depending on the application. Although the alchemy ink is more expensive than the traditional conductive inks, the more expensive alchemy ink could cost less per device because of the alchemy ink’s resistivity.
What are Conductive Inks Used For?
Conductive inks can be used for flexible circuits,3D antennas, flexible hybrid electronics, EMI shielding, and other printed electronics applications. ACI Materials’ alchemy conductive inks are already in use in several different markets.
CHASM Advanced Materials utilizes alchemy inks to develop transparent heaters. These heaters are used in the automotive and industrial industries. The alchemy conductive inks are used to create the busbar system for the heater with low sheet resistance. The alchemy conductive ink allows for larger and more powerful heaters to be printed.

Alchemy conductive inks can also be used to print finer features on rougher surfaces during 3D printing. Inks can be micro-dispensensed with no leakage. These conductive inks reduce prototyping times by allowing a direct-write printer to produce parts rapidly. NScyrpt currently uses ACI Materials’ alchemy inks to print a fully functional cylindrical acoustic sensor platform equipped with Bluetooth communication.
Ready to Get Started with Conductive Inks?
ACI Materials is continuously developing and improving functional materials for printed electronic manufacturers. If you’re looking to replace your traditional PTF conductors or try out our alchemy inks for a new printed application, reach out to our team today.